profinet开发必备文件,介绍profinet的协议内容,英文原版文档
Application Layer services for decentralized periphery and distributed automation Specification for PROFINET
1 Scope
2 Normative references
3 Terms, definitions, abbreviations, symbols and conventions
4 Concepts
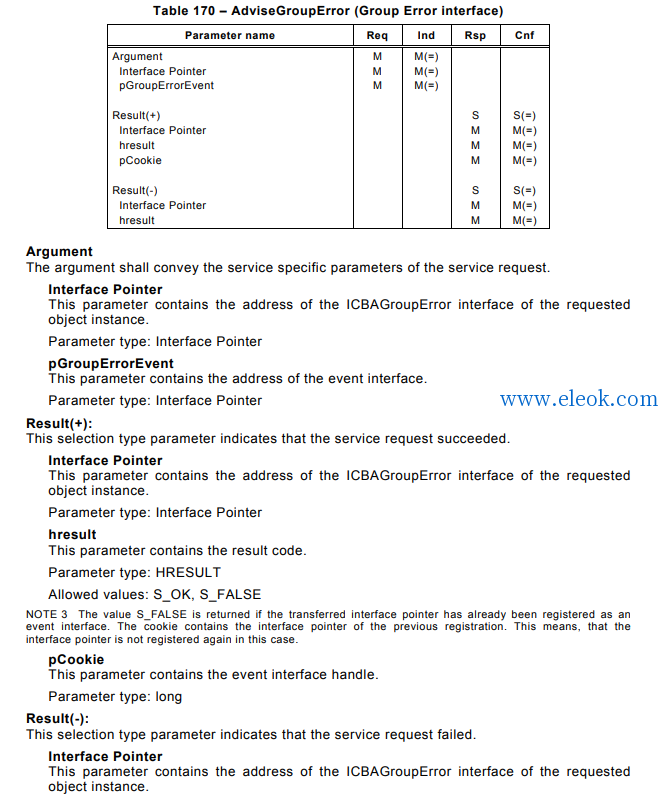
5 Data type ASE
6 Communication model for common services
7 Communication model for distributed automation
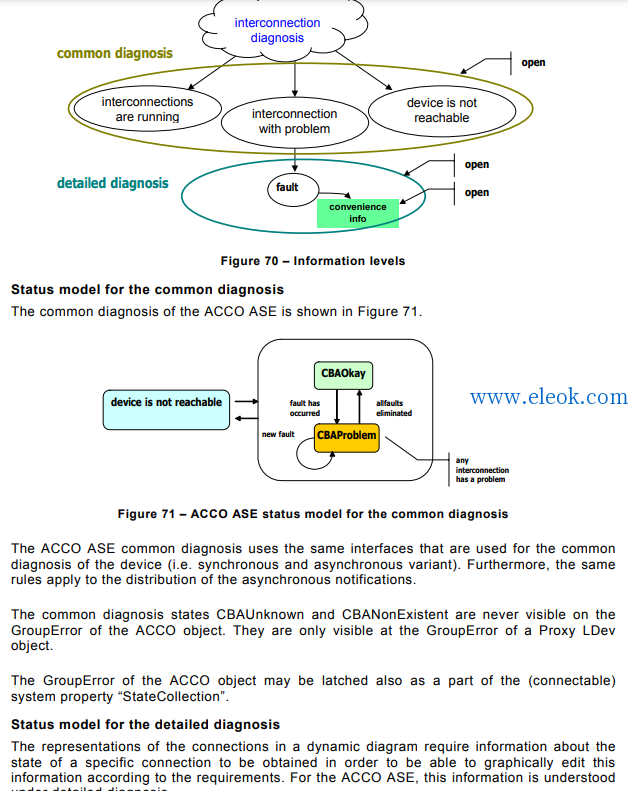
8 Communication model for decentralized periphery
文档:版权说明:本文档由用户提供并上传,仅供个人学习用途,若内容存在侵权,请联系我们删除。
 profinet协议 PN-AL-Services_2712_V22_Oct07.pdf
(3.46 MB, 售价: 5 E币)
profinet协议 PN-AL-Services_2712_V22_Oct07.pdf
(3.46 MB, 售价: 5 E币)
【必读】版权免责声明
1、本主题所有言论和内容纯属会员个人意见,与本论坛立场无关。2、本站对所发内容真实性、客观性、可用性不做任何保证也不负任何责任,网友之间仅出于学习目的进行交流。3、对提供的数字内容不拥有任何权利,其版权归原著者拥有。请勿将该数字内容进行商业交易、转载等行为,该内容只为学习所提供,使用后发生的一切问题与本站无关。 4、本网站不保证本站提供的下载资源的准确性、安全性和完整性;同时本网站也不承担用户因使用这些下载资源对自己和他人造成任何形式的损失或伤害。 5、本网站所有软件和资料均为网友推荐收集整理而来,仅供学习用途使用,请务必下载后两小时内删除,禁止商用。6、如有侵犯你版权的,请及时联系我们(电子邮箱1370723259@qq.com)指出,本站将立即改正。
|